
Think of it like opening a shop. You could put it on a busy street or a quiet alley. The busy street gets more foot traffic. SEO puts your website on that busy street.
When someone types a question into Google, your content can show up. Not by gaming the system. Just by being genuinely useful and easy to find.
Why bother with SEO? Because most people still find websites through search. Social media changes constantly. Ads cost money every day. But good rankings bring free traffic month after month.
This guide works for beginners and experts alike. Start from scratch or skip to advanced topics. Either way, you’ll walk away with tactics that actually work.
One thing to know upfront: SEO takes time. You won’t rank overnight. But if you stick with it, you’ll see real results.
SEO stands for search engine optimization.
In plain English, it means making your website easy for search engines to understand. And easy for people to find.
Most people get this wrong. SEO is not about tricking Google. It’s about helping people.
When you optimize your site, you do two things. First, you help Google figure out what your page is about. Google scans words, links, and the structure of a page to understand its content. Clear organization helps.
Second, you help real people decide to click. When someone searches for “how to bake bread,” they see ten results. Your title needs to stand out. If it sounds helpful, they click. If it sounds spammy, they skip it.
Good SEO does both. The search engine finds you. The person trusts you. You get the click.
To rank well, you need to understand how search engines work. Don’t worry. This is simple.
Search engines use bots. Some people call them spiders or crawlers.
These bots visit websites. They follow links from page to page. They scan constantly, looking for new content or updates.
If your page has no links pointing to it, bots can’t find it. That’s why internal linking matters. Connect all your important pages.
After crawling, the search engine decides whether to index your page.
Indexing means adding it to the database. Once indexed, it can show up in results. If not indexed, it stays invisible.
Not every page gets indexed. Duplicate content blocks it. Low-quality blocks it. Technical problems block it. Monitor which pages make it into the index.
Once indexed, your page enters the ranking competition.
When someone searches, Google checks hundreds of signals. Content quality matters. Backlinks matter—page speed matters. User experience matters.
The goal is simple. Higher rankings mean more visibility. More visibility means more clicks.
Just because a page is indexed doesn’t mean it ranks well.
Google wants pages that match search intent. Pages that provide real value. Pages from trustworthy sites. If yours doesn’t meet those standards, it gets buried on page 10.
SEO has different parts. Each one matters.
This is everything on your website. Your content. Your titles. Your headings. Your images. Your links.
Example: You run a bakery site. Your blog post is titled “How to Bake Sourdough Bread at Home”. You use clear headings. You add helpful images. You link to related recipes. That’s on-page SEO.
This is what happens outside your site.
The biggest part is backlinks. That’s when other websites link to yours. These links work like votes. More quality links mean more trust from Google.
Example: A food blog mentions your sourdough recipe and links to it. That backlink tells Google your content is worth sharing.
This is behind-the-scenes work. Site speed. Mobile friendliness. Crawlability. Security.
Example: Your site takes 10 seconds to load. People leave before seeing your content. Google notices. Your rankings drop. Fixing that speed problem is technical SEO.
If you have a physical business, this matters.
Local SEO helps you show up for location searches. Someone types “bakery near me.” Your shop appears on Google Maps with reviews and directions. That’s local SEO working.
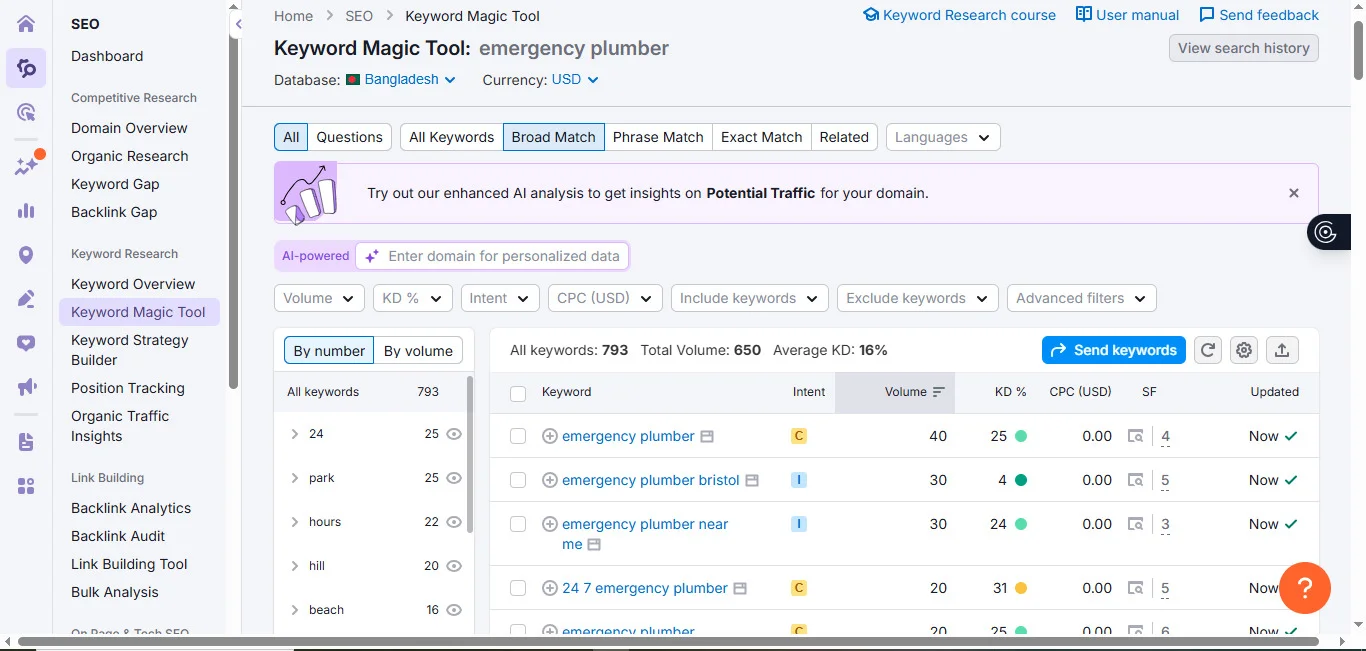
Everything starts with keyword research.
Before writing anything, you need to know what people actually search for.
You could write the best article ever. But if nobody searches for that topic, nobody finds it. Keyword research shows what your audience wants. It guides your content.
Search intent is the reason behind a search. What does the person want?
Understanding intent helps you create the right content for the right people.
Informational: The person wants to learn. Example: “What is SEO?” or “How to bake bread.”
Commercial: The person is researching before making a purchase. Example: “best SEO tools” or “top bread makers”.
Transactional: The person is ready to buy. Example: “buy SEO software” or “order bread online”.
Navigational: The person wants to go to a specific site. Example: “Enneaagon SEO tools” or “Google Search Console”.
Start with Google search suggestions. Type a word into Google. It shows you related searches. These are real queries people use.
Check the “People Also Ask” boxes. These questions show what users want to know. Each one is a potential keyword.
Look at competitor pages. See what keywords they target. Check their titles and headings. You’ll spot patterns and gaps.
Use SEO tools when ready. Keyword research platforms show search volume and difficulty. They speed things up once you know the basics.
Your competitors already rank where you want to be. Instead of guessing, learn from what Google already rewards.
Google picked them for a reason. Study top-ranking pages. You’ll see what quality looks like in your niche.
But don’t copy them. Learn why Google chose them. Then make something better.
Your SEO competitors might not be your business competitors.
They’re whoever ranks for your target keywords. Search your keyword. The top five to ten results are your SEO competitors for that query.
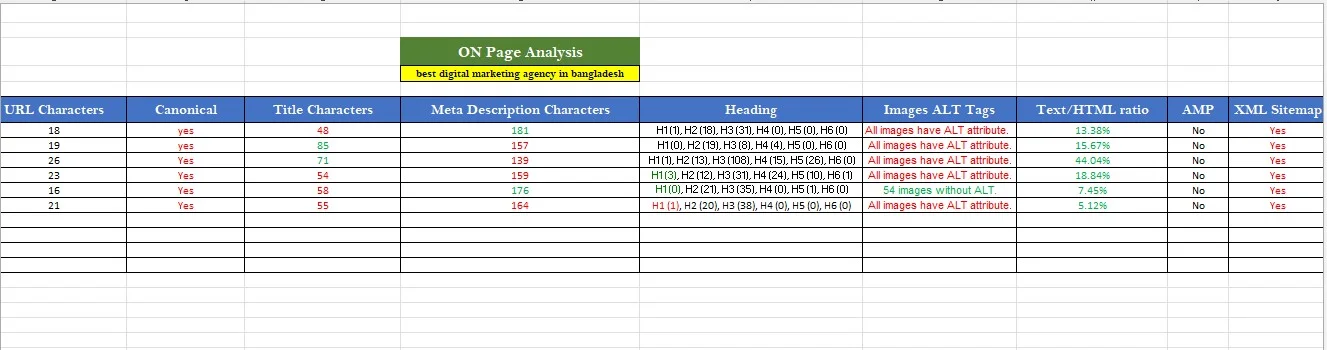
Content structure: How do they organize information? What headings do they use? How long is the content?
Keywords: What terms appear in titles and headings? Are they targeting the same keywords as you?
Backlinks: Who links to them? Quality backlinks boost authority. Strong link profiles explain high rankings.
Page quality: Is the content detailed? Do they use images or videos? What makes their page better than yours right now?
Take notes. Find gaps. Then create content that deserves to outrank them.
On-page SEO is where you have the most control. Everything on your page affects ranking.
Your title tag shows up in search results. It needs to be clear and interesting. Put your main keyword near the start. Keep it under 60 characters. Make it natural, not stuffed.
This appears under your title in the results. It doesn’t directly affect rankings. But it affects clicks. Write a clear summary. Use action words. Give people a reason to click. Keep it under 155 characters.
Headings give structure to your content. They help readers scan the page and help search engines understand what each section is about.
Every page should have one H1, which is your main title. Below that, break your content into clear sections using H2 headings. If a section needs further explanation, use H3 headings as subsections.
Heading order matters. Skipping levels confuses both users and search engines.
Incorrect structure:
H1 → H3 → H5 → H2
Correct structure:
H1 → H2 → H3 → H4 → H5 → H6
Always place H2 headings directly under the H1, and H3 headings under their related H2. This logical hierarchy improves readability, accessibility, and SEO performance.
When headings are used properly, your content becomes easier to understand, easier to navigate, and easier for Google to rank.
Keep URLs short and readable. Use hyphens between words. Include keywords when natural.
Example:
Good URL: seotools.enneaagon.com/keyword-research
Bad URL: seotools.enneaagon.com/p?id=12345
Link to other pages on your site when relevant. This helps users find related content. It helps Google understand your structure.
Use natural anchor text. Not “click here.” Try “learn more about keyword research” instead.
Images make content better. But they need optimization.
Compress image files so they load fast. Use descriptive file names.
These are the better image sizes for websites. Add alt text that describes the image. Don’t stuff keywords. Just describe what’s there.
This matters most.
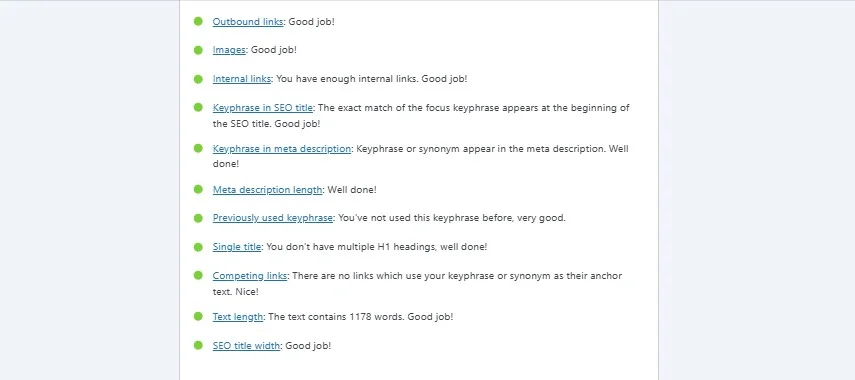
Google wants helpful content written by real people for real people. Answer questions fully. Provide examples. Make it easy to read.
Write like you’re talking to a friend. Don’t stuff keywords. Write for humans, not robots.
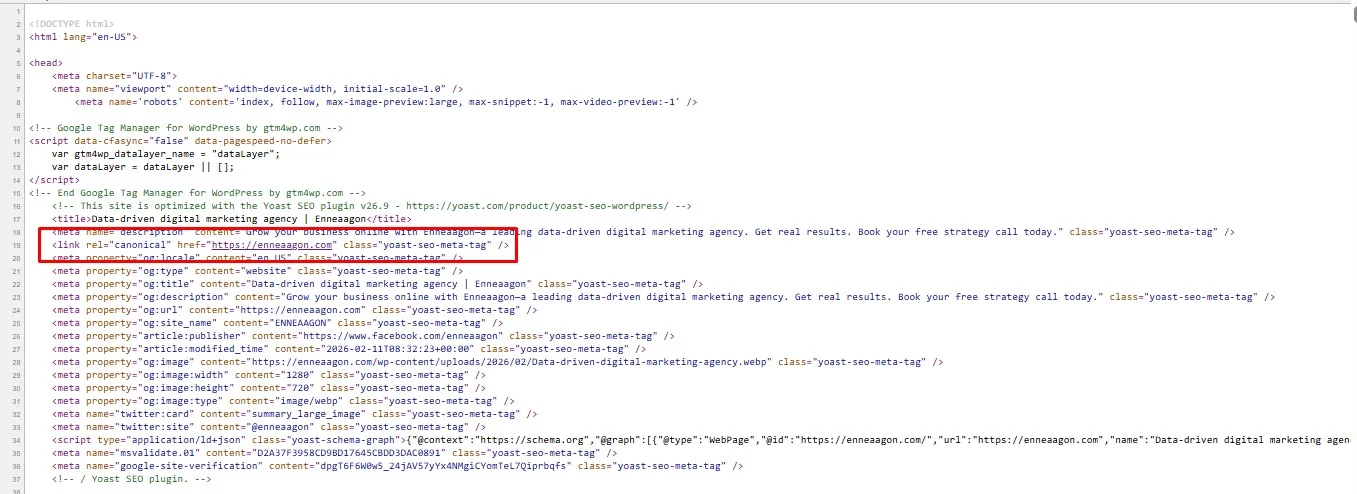
Canonical Tags Are Important for Website Pages:
💡 Tip: For pages like Home, About, Contact, or Services, usually the canonical URL is the same as the page URL itself—unless there’s a duplicate copy somewhere else (like a printer-friendly version or tracking URL).
How to add a canonical tag:
Add this in the <head> section of the page’s HTML:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.yourwebsite.com/>
Technical SEO makes sure search engines can crawl and index your site. You don’t need to be a developer.
If search engines can’t crawl your pages, they can’t index them. Check for broken links. Fix redirect chains. Make sure important pages are accessible.
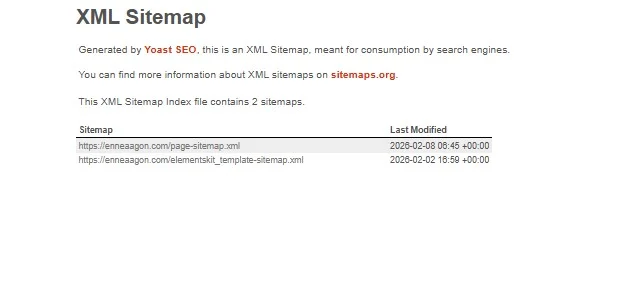
A sitemap lists all your pages. It helps search engines find content faster. Most website platforms create sitemaps automatically. If you have a WordPress website, then use the Yoast SEO plugin. It will build your website’s XML sitemap automatically. Submit the XML sitemap to Google Search Console.
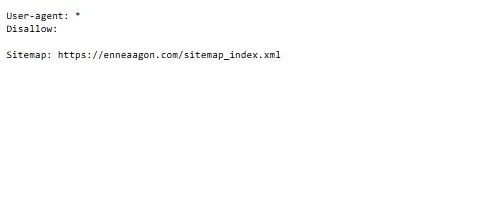
This is an instructor for search engines. This file tells search engines which pages to crawl and skip.
Use it to block low-value pages like admin panels. Be careful. Blocking the wrong pages hurts rankings.
Pro Tip: Always include your XML sitemap link in your robots.txt file. When Google starts crawling your website, it checks robots.txt first. By listing your sitemap there, you make it easier and faster for Google to discover all your pages, helping them get indexed more efficiently.
Example:
Sitemap: https://www.yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml
This simple step ensures Google knows exactly where to find your content, giving your SEO a little boost right from the start.
Slow sites lose visitors and rankings. Compress images. Use good hosting. Minimize unnecessary code. Check Google PageSpeed Insights for fixes.
Most searches happen on phones. Your site must work perfectly on mobile. Use responsive design. Test on different screen sizes. If your site is broken on a mobile screen, then you will lose visitors, and it also hurts SEO & Google rankings.
These are Google’s user experience measurements. Loading speed. Visual stability. Interaction speed. You don’t need perfect scores. Just avoid the terrible ones. Fix major issues first.
This is code that helps search engines understand content better. It enables rich results like star ratings and FAQ snippets. Many SEO plugins handle this automatically. Focus on the basics to start.
Off-page SEO is mostly about backlinks. But it’s also about building trust outside your site.
A backlink is when another website links to yours. Think of it like a vote. More quality sites linking to you means more trust from Google. Not all backlinks are equal. One link from a respected site beats a hundred from random blogs.
Years ago, people spammed backlinks to rank. Google caught on. Now, low-quality links can hurt you. Focus on earning links from relevant, trusted, real sites.
Create shareable content. Write guides, research, or resources so helpful that people naturally want to share them. Guest posting. Write articles for other sites in your industry. Include a link in your bio or content when relevant. Brand mentions. Sometimes people mention your brand without linking. Reach out and ask politely for a link. Never buy links. Google penalizes this hard. You might see a short boost. Then your rankings crash. Build links the right way.
If you run a local business, local SEO puts you on the map. Literally.
Anyone serving customers in a specific area. Bakeries. Plumbers. Law firms. Anything with a physical location. When someone searches “SEO agency near me” or “best coffee in Chicago”, local SEO determines who shows up.
Claim and verify your Google Business Profile. Fill out every section. Add address, phone, hours, and photos. Keep it updated. Your profile appears in Maps and local results. Complete profiles rank higher.
NAP stands for Name, Address, Phone. These details must match everywhere. Your website. Google Business Profile. Social media. Directories. Inconsistent info confuses Google and hurts rankings.
Include your city in keywords. Not just “SEO services”. Try “SEO services in Austin” or “Austin SEO agency”. Use these naturally in titles, content, and meta descriptions.
Google values reviews. More reviews, especially positive ones, improve local rankings. Ask happy customers to leave reviews. Respond to all reviews. Good and bad. It shows you care.
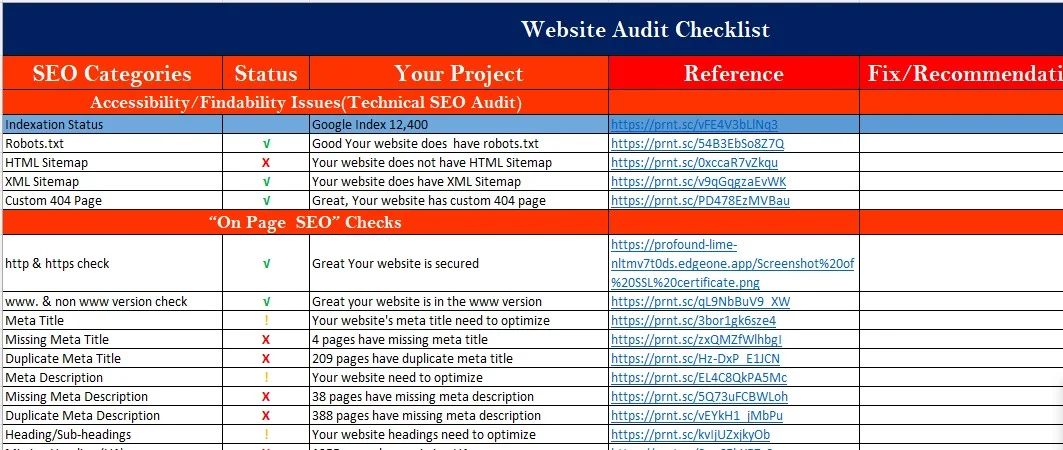
An SEO audit is a health check for your website. It finds problems and opportunities.
It’s a detailed review of your SEO performance. You check technical issues. Content quality. Keywords. Backlinks. User experience.
Small issues can tank rankings. A broken link here. A slow page there. It adds up. Audits catch these problems early.
Technical issues: Broken links. Slow pages. Mobile problems. Crawl errors. Fix these first.
Content issues: Thin content. Duplicate pages. Missing titles or descriptions. Update or remove weak content.
Keyword gaps: Are you targeting the right keywords? Are competitors ranking for terms you’re missing?
User experience: Is your site easy to navigate? Do people leave quickly? Bad experience kills conversions and rankings.
Run audits regularly. Every few months is smart. Sites change. Google changes. Competitors change. Stay on top of it.
Everyone hits roadblocks. Here are the most common problems.
Your pages don’t show up anywhere. Usually means they’re not indexed. Or you’re targeting the wrong keywords. Or your site is too new.
Your traffic suddenly falls. Check if Google released an algorithm update. Look for technical issues. Sometimes competitors just outrank you.
You publish content, but it doesn’t appear in search. Check robots.txt. Make sure you didn’t block crawlers. Submit your sitemap to Search Console. Also, remove the no-index tag from your website.
Slow sites lose visitors and rankings. Compress images. Upgrade hosting. Remove unnecessary plugins.
Nobody links to your site. Create content worth sharing. Reach out to people in your industry. Guest post. Build relationships.
You’re ranking for keywords nobody searches. Go back to keyword research. Target terms with real search volume. These problems are fixable. Diagnose the issue. Make a plan. Solve it step by step.
Now let’s fix those problems.
Check Google Search Console. It shows which pages are indexed. If pages are blocked, update robots. txt. If they’re not crawled, add internal links. Submit your sitemap. Request indexing for important pages.
If content doesn’t rank, make it better. Add detail. Include examples. Answer real questions. Remove fluff. Look at what ranks now. What do those pages do well? Match or beat their quality.
Start keyword research over. Find terms people actually search. Match search intent. Target long-tail keywords if you’re new. They’re easier to rank for and bring qualified traffic.
Check if Google rolled out an update. Read what changed. If traffic dropped because of an update, your content might not meet new standards. Fix technical errors. Improve quality. Build better links. Recovery takes time. But it happens if you do the work.
SEO takes time. New sites can take three to six months to start ranking. Don’t make constant changes out of impatience. But if something is broken, fix it immediately. Pages not indexing. Site down. Major errors. Trust your judgement.
AI is changing search. Google now shows AI-generated overviews at the top of many results.
What does this mean for SEO?
Google’s AI pulls info from top pages and summarizes it. Users get answers without clicking. But people still click for detailed answers, how-tos, and expert opinions. AI handles simple questions. Your content handles everything else.
If your content appears in these overviews, you get massive visibility. How? Provide clear, direct answers. Use structured headings. Write concisely. The same principles that worked before still work now.
With AI summarizing basic info, shallow content loses value. You need depth. Real insights. Original perspectives. AI can generate content. But it can’t replace human experience. Show expertise. Share personal stories. Provide an analysis that AI can’t replicate.
Use AI for research. For keyword ideas. For outlines. But don’t let AI write your final content. Edit heavily. Add your voice. Make it yours. Google can spot generic AI content.
People often confuse SEO and SEM. Here’s the difference.
Factor | SEO | SEM |
Traffic Type | Organic (free) | Paid (ads) |
Cost | Time and effort | Pay per click |
Speed | Slow (months) | Instant |
Long-term Value | Builds over time | Stops when the budget ends |
Trust | Higher (earned) | Lower (paid) |
SEM (search engine marketing) includes both SEO and paid ads. But when people say SEM, they usually mean paid search.
SEO builds long-term traffic. SEM gives instant visibility. Most businesses use both. Start with SEO as a foundation. Add SEM when you need faster results.
Here’s what you learned:
SEO is a skill you build over time. It’s work. Smart work.
Anyone can learn it. You don’t need to be a developer or marketing genius. You just need to understand how search works and stay consistent.
Focus on users first. Google’s job is to show people the best results. If your content genuinely helps, you’ll get rewarded.
Don’t chase shortcuts. Tricks might work for weeks. Then they backfire. Build something real. Build something sustainable.
Consistency beats perfection. You don’t need to do everything at once. Start with the basics. Master keyword research. Write quality content. Fix technical issues. Build links slowly. Keep improving.
SEO changes. But core principles stay the same. Be helpful. Be clear. Be trustworthy. Do that well, and rankings follow.
You have the roadmap. Go use it.
“We use cookies to enhance your experience on our website. By continuing to browse, you agree to our use of cookies. You can manage or disable cookies in your browser settings at any time.”
Manage your cookie preferences below:
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.